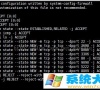
PostgreSQL不允许将所有权限赋给匹配到表一级的所有数据库对象,需要为每一个新建的表授予权限。
使用数据表
创建数据表
在创建新表前确保用管理员用户账户(MySQL中的root用户,PostgreSQL中的postgres用户)登录来创建表
MySQL和PostgreSQL的数据类型
数据类型 描述
char 定长字符串值
varchar 变长字符串值
int 整数值
float 浮点值
Boolean 布尔类型true/false值
Date YYYY-MM-DD格式的日期值
Time HH:mm:ss格式的时间值
Timestamp 日期和时间值的组合
Text 长字符串值
BLOB 大的二进制值
使用CREATE TABLE建立表
[plain]
test=# CREATE TABLE employees (
test(# empid int not null,
test(# lastname varchar(30),
test(# firstname varchar(30),
test(# salary float,
test(# primary key (empid));
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE / PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "employees_pkey" for table "employees"
CREATE TABLE
test=# dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+-----------+-------+----------
public | employees | table | postgres
(1 row)
在psql中还需要在表一级分配权限。
[plain]
test=# GRANT SELECT,INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE ON public.employees TO su;
GRANT
以postgres登录角色来执行,并连接到test数据库,且必须指定模式名。
插入和删除数据
关于SQL部分,这里不做详细笔记。
[plain]
mysql> CREATE TABLE employees (
-> empid int not null,
-> lastname varchar(30),
-> firstname varchar(30),
-> salary float,
-> primary key (empid));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO employees VALUES (1,'Blum', 'Rich', 1234.5);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
查询数据
[plain]
mysql> SELECT * FROM employees;
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
| empid | lastname | firstname | salary |
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
| 1 | Blum | Rich | 1234.5 |
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在脚本中使用数据库
连接到数据库
对于psql:
[plain]
$ cat psql_connection
#!/bin/bash
psql=`which psql`
sudo -u postgres $psql
$ psql_connection
could not change directory to "/home/su1216/android/source/linux_learned"
psql (8.4.17)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=#
对于mysql:
[plain]
$ cat mysql_connection
#!/bin/bash
mysql=`which mysql`
$mysql "test" -u "test" -p
$ mysql_connection
Enter password:
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 38
Server version: 5.1.72-0ubuntu0.10.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
执行脚本时,mysql会停下来要求用户输入密码,这个问题可以避免。
下面是一种糟糕的方式,直接将密码放在脚本中明文显示:
[plain]
$ cat mysql_connection
#!/bin/bash
mysql=`which mysql`
$mysql "test" -u "test" -ptest
-p与密码紧密相连。
另一种解决方案:
mysql使用$HOME/.my.cnf文件来读取特殊的启动命令和设置。
如果没有这个文件,我们自己建立一个即可
[plain]
$ touch /home/su1216/.my.cnf
$ gedit /home/su1216/.my.cnf
$ chmod 400 /home/su1216/.my.cnf
.my.cnf内容如下
[plain]
$ cat /home/su1216/.my.cnf
[client]
password = test
现在再执行mysql_connection就不会要求输入密码了
向服务器发送命令
1.发送一个命令并退出
2.发送多个命令
对于mysql,可以使用-e选项:
[plain]
$ cat mysql_test
#!/bin/bash
mysql=`which mysql`
$mysql "test" -u "test" -ptest -e "select * from employees"
输出结果为:
[plain]
$ mysql_test
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
| empid | lastname | firstname | salary |
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
| 1 | Blum | Rich | 1234.5 |
+-------+----------+-----------+--------+
对于psql,可以使用-c选项
发送多条命令可以使用重定向,注意:最后的EOF所在行不能有其他字符串。
[plain]
$ cat mysql_test
#!/bin/bash
mysql=`which mysql`
$mysql "test" -u "test" -ptest << EOF
show tables;
select * from employees;
EOF
返回的结果是原始数据,没有之前的边框。
多条命令的结果之间没有分隔符
[plain]
$ mysql_test
Tables_in_test
employees
empid lastname firstname salary
1 Blum Rich 1234.5
对于psql也适用,但是返回的结果是有边框的。
[plain]
$ cat psql_test
#!/bin/bash
psql=`which psql`
sudo -u postgres $psql << EOF
c test;
select * from employees;
EOF
输出结果:
[plain]
$ psql_test
could not change directory to "/home/su1216/android/source/linux_learned"
You are now connected to database "test".
empid | lastname | firstname | salary
-------+----------+-----------+--------
1 | Blum | Rich | 1234.5
(1 row)
格式化数据
将结果集赋给变量:
[plain]
#!/bin/bash
mysql=`which mysql`
results=`$mysql "test" -u "test" -Bse 'show databases'`
for result in $results
do
echo "$result"
done
其中-B指明了mysql使用批处理模式(禁止了格式化符号)
-s(silent)使得列标题被禁止掉
使用格式化标签
psql和mysql都使用-H来以HTML格式显示结果
[plain]
$ mysql "test" -u "test" -He 'select * from employees'
<TABLE BORDER=1><TR><TH>empid</TH><TH>lastname</TH><TH>firstname</TH><TH>salary</TH></TR><TR><TD>1</TD><TD>Blum</TD><TD>Rich</TD><TD>1234.5</TD></TR><TR><TD>2</TD><TD>Blum</TD><TD>Poor</TD><TD>321.099</TD></TR></TABLE>
mysql还可以以XML格式显示结果
[plain]
$ mysql "test" -u "test" -Xe 'select * from employees'
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<resultset statement="select * from employees
" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<row>
<field name="empid">1</field>
<field name="lastname">Blum</field>
<field name="firstname">Rich</field>
<field name="salary">1234.5</field>
</row>
<row>
<field name="empid">2</field>
<field name="lastname">Blum</field>
<field name="firstname">Poor</field>
<field name="salary">321.099</field>
</row>
</resultset>
本文来自系统大全为您提供如需转载请注明!推荐win10下载